Clinicians will examine the health of your eyes, looking for signs of cataract, glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration as well as general health problems which sometimes affect the eyes first.

Eye irrigation is used to flush particles and harmful chemicals from the conjunctiva and cornea. Eyelid eversion is used to expose the superior palpebral conjunctiva and fornix, so that foreign matter can be identified in these areas.
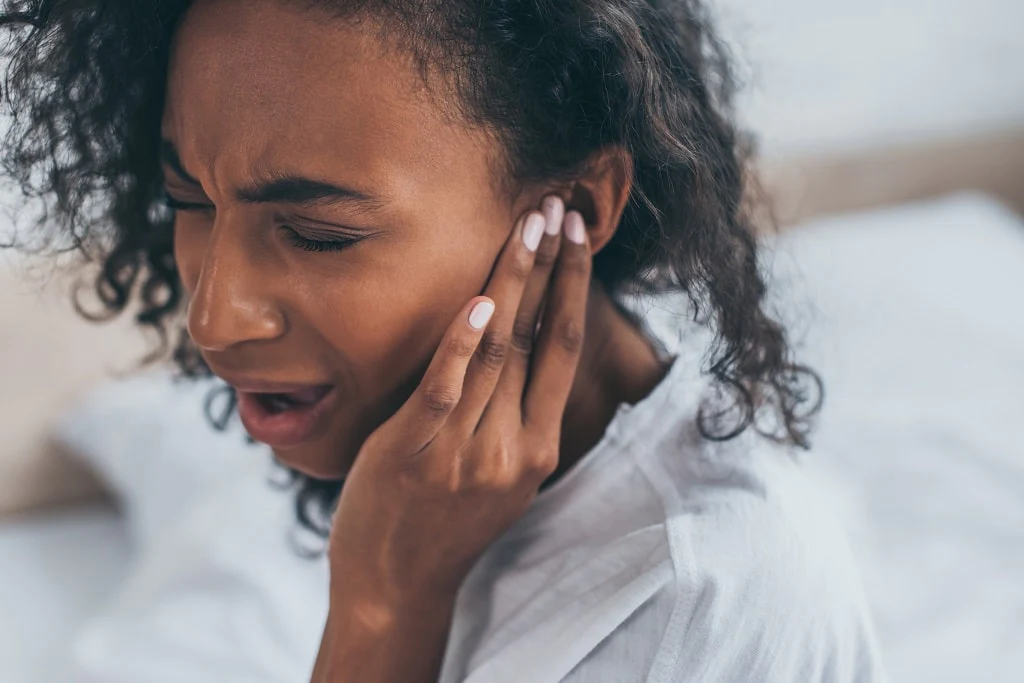

Ear irrigation involves using water, saline, or oil to clear out extra wax in your ear. While it’s generally a safe process, it’s not uncommon to experience some dizziness and other symptoms afterward.
Ear irrigation is a routine procedure used to remove excess earwax, or cerumen, and foreign materials from the ear.
The ear naturally secretes wax to protect and lubricate the ear as well as to keep debris out and hinder bacterial growth. Under normal conditions, the body keeps the amount of earwax in the ears under control. Too much earwax or hardened earwax can cause a blockage in the ear, resulting in earaches, ringing in the ears, or temporary hearing loss.